Simulation Training: 8 Reasons to Use Mobile Units for Simulation Training
For the past twenty-five years, there has been a significant increase in the use of simulation-based training for healthcare providers. Today, simulation technology advancements have become a primary component of medical education. With the increasing complexities in healthcare, simulation-based training (SBT) enhances clinical skills and patient safety.
Furthermore, simulation training in mobile health clinics continues to enhance workforce development and healthcare education in the professional community well beyond brick-and-mortar facilities. Healthcare professionals increasingly use mobile sim labs for in situ hands-on practice of various modalities in diverse settings. They are frequently used by practitioners who work in underserved areas. These fully equipped MHCs have simulation equipment on board mobile laboratories that travel to communities to train nurses, doctors, first responders, and technicians in real-life settings without taking risks with actual patients. Along with providing continuing education, they are particularly valuable for use in perfecting skills in less frequently performed procedures.
1. Expand Your Reach: Accessibility and Geographical Reach

Mobile health clinics provide a highly efficient way to expand simulation training opportunities to rural, urban and underserved communities. Teaching hospitals or educational centers are typically inaccessible to those working in these areas. By bringing training directly to practitioners and front-line responders who lack easy access, mobile clinics bridge the gap in medical training and ensure a more equitable distribution of learning resources.
2. Adapt Quickly to Change: Adaptability and Flexibility
Mobile simulation training units are designed to be adaptable to various scenarios. Their flexibility allows trainers to tailor simulations to individual learners and reflect actual scenarios faced by primary care, obstetrics, surgery, gynecology, pediatrics, emergency response and virtually any other medical discipline. The techniques and technologies employed in mobile SIM labs offer a highly adaptable environment for providing services that mirror a permanent simulation center.
3. Bring High-Tech Equipment Everywhere: Enhanced Training Realism & Technology
Mobile health clinics that are equipped with high-fidelity simulation technology, including interactive software and virtual reality tools, provide learning experiences with realistic manikins replicating human anatomy and easy-to-use training tools for healthcare simulation. These MHCs go into the field to deliver realistic, hands-on practice in a controlled and immersive environment to improve healthcare professionals’ clinical decision-making and teamwork skills.
A mobile simulation center transports equipment and facilitators so learners can experience healthcare simulation scenarios with virtual reality devices, patient manikins, task trainers, and other simulation resources. The highly trained mobile simulation center staff do on-site set-ups and provide learners with hands-on lessons for each clinical simulation occurrence they face in the real world.
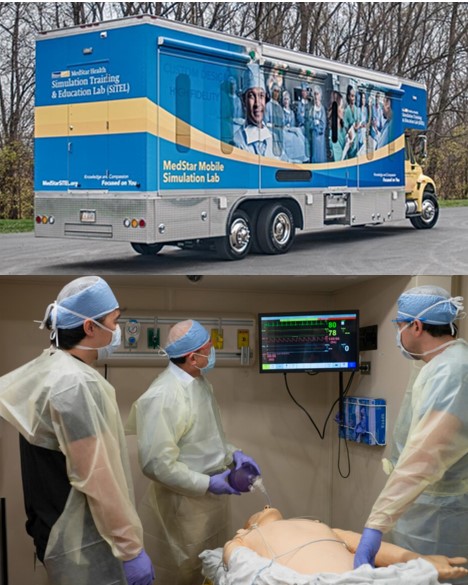
Mobile sim units often incorporate digital cameras to film trainees for post-lesson debriefing. Training sessions can range from brief rescue breathing exercises to several hours of obstetrics instruction. Mobile simulation training can also be used to obtain American Heart Association Certification. Certification is obtained from simulated instruction with Heartsaver® and Basic Life Support (BLS), which provides advanced cardiac and pediatric life support training.
However, in recent years, the technology landscape has changed. Some areas at the forefront of today’s technologies in simulation training include:
- Virtual reality (VR) creates realistic and interactive training environments for healthcare professionals conducting medical simulations.
- Mixed reality (MR) provides interaction with a combination of virtual and physical to create highly realistic training scenarios for learning and practicing skills in a safely controlled environment.
- Customizable AI-enabled virtual patients allow users to replicate high-fidelity simulations. This new technology merges advanced artificial intelligence with virtual reality to provide simulation programs with interactive experiences that are scalable and cost-effective.
- Extended Reality (XR) is a term that encompasses all immersive technologies, such as virtual reality (VR), mixed reality (MX), and augmented reality (AR) simulation. AR combines real and virtual imagery in real-time. Each XR technology represents advanced techniques for learners to increase their knowledge and skills far beyond what was possible just a few years ago.
Advancements in Mobile Medical Simulation with Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare simulation is relatively new, yet has proven to provide significant advancements, including its use in mobile SIM labs. AI in mobile medical simulation clinics brings the most advanced technologies into the field to train remote learners. Educational modalities that incorporate AI-based learning are changing the landscape of healthcare simulation. AI can help diagnose conditions, provide treatment recommendations, and increase medication administration safety. It can help learners improve patient care by acting as virtual medical assistants, creating medical notes, and predicting the occurrence and progression of chronic diseases.
Its creation of algorithms in software is similar to the way humans think and make decisions. Because of AI’s growing advancements in patient care in hospitals, clinics, and doctors’ offices, it’s a natural progression in mobile clinics for the benefit of training field personnel in state-of-the-art technologies.
AI does not replace professional trainers; instead, it creates dynamic and adaptive virtual patients in mobile health simulation clinics for practicing decision-making and improving clinical skills by working with realistic AI-driven patient scenarios. The trainer and student get real-time responses to interventions that provide individualized feedback, which adapts to situations based on the learner’s choices. This effectively tailors the simulation experience to an individual’s learning requirements.
4. Expand Multidisciplinary Training
Mobile SIM labs facilitate training across various healthcare disciplines. Nurses, doctors, dentists, EMTs, paramedics, firefighters, police officers, correctional facility nurses, and allied health professionals can work together in environments that simulate real-life complex conditions. For example, police, firefighters, and EMTs are frequently at the scene of an emergency. In addition, doctors, nurses, and other allied health professionals are on the same team when treating patients. Mobile Simulation Labs provide a collaborative approach that fosters communication skills and teamwork, which is critical in patient care.
5. Generate Real Savings: Profitability
Permanent simulation centers in hospitals or universities are essential for centrally located staff. However, they are expensive to build and operate. Conversely, mobile health clinics offer a more cost-effective alternative. They can be shared among various communities and institutions, thus spreading the cost. Mobile simulation labs optimize resources and serve as a significant revenue source without compromising training quality.
They are profitable when strategically operated to facilitate diverse training needs across different settings, such as medical colleges, universities, and those providing emergency medical services in rural communities. Income is generated by securing contracts with paying clients to provide training services beyond the operator’s primary institution.
6. Be Prepared: Emergency Mass Casualties
Mobile health clinics are often used to train healthcare workers to respond to public health emergencies such as natural disasters or pandemics. They can also simulate mass vaccination drives and triage during a crisis to determine the urgency and nature of treatments and other emergency interventions, enhancing response capabilities.
7. Expand Your Continuing Education Program by Refreshing Skills
Medical professionals already in practice can refresh their skills in mobile clinics, which offer a convenient way to learn new technologies and techniques and practice old ones without having to travel far from their home base.
8. Establish Base-Line Performance Standards: Data Collection and Feedback Integration
Mobile health clinics can collect data on training performance. Techniques are employed to help refine learning strategies and customize learning modules for the individual. Immediate feedback during simulations leads to faster skill development and better knowledge retention.
Conclusion
The increased use of simulation training in mobile health clinics exhibits an innovative shift in medical education. Mobile SIM labs prioritize accessibility, flexibility, and preparedness. As the use of mobile clinics continues to grow, we will see technological advances that will play an essential role in shaping a well-trained and resilient healthcare workforce. Taking simulation training out to the field where the action is will help us to identify needs that may be overlooked in a hospital setting.
Sources Include: